Published on July 19, 2023
Tata Power has introduced the concept of step change and safety intervention to take organisational safety to the next level. All divisions of the three clusters participated in the step change and intervention initiatives.
What is Step Change? A significant change, especially one that results in significant improvement in performance. Examples include new products/tools/equipment/technology/automation/mechanisation available to manage workplace Health & Safety risks.
What is Safety Intervention: Safety intervention is an attempt to change how things are done to improve safety. Within the workplace, it could be any new programme, practice, or initiative intended to improve safety (e.g., engineering intervention, special training programme, administrative procedure, etc.).
At the organisation level, Tata Power has introduced 253 interventions of which 66 are step change and 187 are safety interventions. It is presented in a graphical form as below.
Year-wise implementation of technologies is given in the table below
Table 1: Year-Wise Technology Implementation
| Year | Step change | Safety interventions | Total | Horizontal deployment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FY21 | 54 | NA | 54 | NA |
| FY22 | 51 | 158 | 209 | NA |
| FY23 | 66 | 187 | 253 | 101 |
| FY24 | 03 | 16 | 19 | 22 |
| Total | 174 | 361 | 535 | 133 |
Graph 1: Showing Technology Interventions Implemented at Tata Power in FY 23
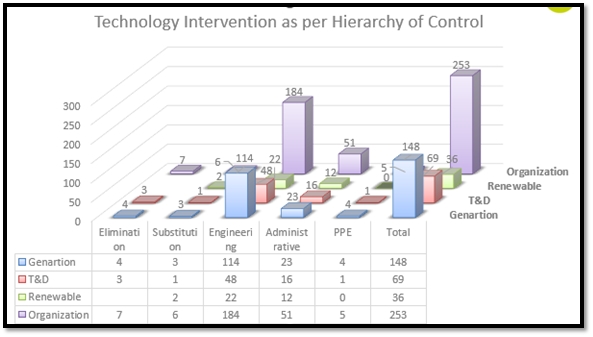
Out of total 253 interventions, 7 are related to elimination of risk, 6 are substitution, 184 are engineering control, 51 are administrative and 5 are related to PPE.
Due to implementation of these intervention at organisation level, high risk jobs are reduced to low risk jobs, the statistics of which are given below.
Table 1: Statistics of Reduction of Risk due to Implementation of Interventions
| Very High Risk (29) | High Risk (129) | Medium Risk (69) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | L | VL | M | L | VL | L | VL |
| 6 | 14 | 9 | 9 | 96 | 24 | 46 | 23 |
| M-Medium , L-Low, VL- Very Low | |||||||
Total 29 very high risk jobs, 129 high risk jobs and 69 medium risk jobs are reduced to medium, low and very low- risk category. Some of the examples of step changes which are introduced in Tata Power are elaborated below.
Examples of Step Changes
- Remote Spiking and Cutting Tool:
Triger for Improvement : Tata Power has u nderground 220 KV to 6.6 KV to LT power cables on Mumbai roads. During cable repair or cable diversion activities, it i s required to cut these cables for making joints. To ensure cables are not live, they are spiked manually by a spiking tool and then cut manually. Due to the requirement of checking physically whether the cable is punctured, there was a risk of an incident if the cable was not spiked properly.
Improvement Adopted :With new remote spiking and cutting tools, the company can remotely spike and cut the cable automatically. Cable jointers will not touch the cable until it is cut into two parts automatically. It eliminates electrocution/burn injury risk to jointers. T his process results in the cutting of the cable within 1.5-2 minutes as compared to earlier manual cutting time of 20 minutes.
- Use of Drone for Inspection of Boiler Sheets:
Trigger for Improvement: Haldia is very prone to c yclones due to which every year there is a challenge of loose sheets at the roof tops of all 16 b oilers. It is a huge task to identify the loose sheets before the cyclone and rectify them. Earlier, to inspect the condition of blue scope sheet of the boiler pent house, Tata Power needed to make scaffolding at a height of 33 meters from the ground, which is a very high risk and costly job .
 Improvement Adopted : One of the Tata Power engineers has designed and developed a drone completely in-house and the same is now being used to inspect such critical locational defects through a high- resolution camera. T he image / live video can be monitored through m obile and laptop by the concerned team members to identify the defects and plan for rectifications in advance, well before the cyclone.
Improvement Adopted : One of the Tata Power engineers has designed and developed a drone completely in-house and the same is now being used to inspect such critical locational defects through a high- resolution camera. T he image / live video can be monitored through m obile and laptop by the concerned team members to identify the defects and plan for rectifications in advance, well before the cyclone.
Other uses of the drone in Tata Power are inspection of t ransmission towers, transmission lines, and external surfaces of penstocks in Hydros. Thus, all the technologies introduced by various divisions of Tata Power have resulted in an improvement of safety at the organis ation level to move to the next orbit.
- Artificial Intelligence based Realtime Safety Analytics (Project ‘Third Eye’)
Trigger for improvement: PPGCL FGD project e xecution site is scattered over a land of 500m X200m , where continuous monitoring of safety for all activities across the site is very difficult for available field engineers and safety personne l . The Tata Power p roject t eam has commissioned a system by implementing an AI-enabled real- time video monitoring system for defined cases of unsafe activities for the Prayagraj FGD Project, providing the required applications software, CCTV cameras, servers, GPU, and license network components.
Description of Improvement: Through advanced a utomation of CCTV image analys is , the organization can create a safe workplace, boost overall productivity, and reduce downtimes by a large margin. This system can also help in monitoring worker behavior, detecting potential hazards, and keeping workmen safe at all times.




